Ground Mount vs Roof Mount Solar Cost Comparison – Which is better?
Nov 27, 2024

As the world moves toward sustainable energy, solar power has emerged as one of the most viable and efficient solutions for reducing electricity costs and decreasing carbon footprints. However, when deciding to install solar panels, homeowners and businesses face a critical choice: should they opt for ground-mounted solar systems or roof-mounted ones? This decision is not just about personal preference or aesthetics but also involves a deep dive into costs, efficiency, space requirements, and long-term sustainability.
The financial implications of choosing between a ground mount and a roof mount system can be substantial. Both installation methods offer distinct advantages, but they also come with their own set of challenges and costs. In this essay, we will explore the key differences in the costs of installing and maintaining ground-mounted versus roof-mounted solar systems, considering both initial investment and long-term financial impact. By analyzing the factors that influence pricing, energy efficiency, space requirements, and maintenance, we will better understand which installation option is best suited for different scenarios.
Ground Mount vs Roof Mount Solar Systems
To understand the cost differences, it’s important to first look at the basic structure of each type of installation. Ground-mounted solar systems are exactly what they sound like—solar panels installed on the ground using a rack or frame structure. These systems often require significant land space and are commonly used for larger properties, farms, or rural areas where land is plentiful. The panels are generally fixed on a mounting structure that can be adjusted to optimize angle and sun exposure, which can result in higher energy yields.
In contrast, roof-mounted solar systems are installed directly on the roof of a building. The panels are secured to the roof using a specialized racking system, which varies depending on the roof's material and pitch. Roof installations are particularly common for residential homes and commercial buildings in urban and suburban areas where space is limited. While roof-mounted systems are often cheaper to install due to fewer structural requirements, they may face constraints in terms of panel positioning because of roof orientation, shading from surrounding structures, and aesthetic considerations.
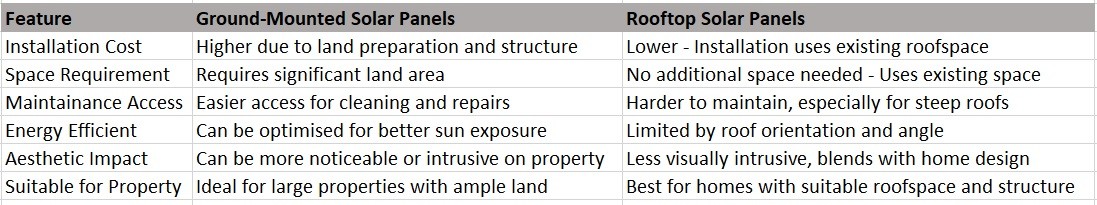
Ground-Mounted vs. Rooftop Solar Panels: Pros and Cons
When choosing between ground-mounted and rooftop solar panels, it's essential to weigh the pros and cons of each option. Ground-mounted systems offer flexibility in panel positioning and are easier to maintain but require more land space and can be costlier to install. Rooftop panels, on the other hand, make use of existing space, reducing installation costs and saving land but may be limited by roof space, orientation, and maintenance accessibility.
Initial Installation Costs
One of the most significant differences between ground-mounted and roof-mounted solar systems is the initial installation cost. Ground-mounted systems tend to be more expensive to install for several reasons.
First, the installation process itself is more labor-intensive. Ground mounts require excavation to install the mounting posts or frames, and often, the land must be cleared and leveled to make space for the panels. This additional labor, combined with the cost of materials like concrete or metal for the frames and posts, leads to a higher overall installation cost. Depending on the complexity of the installation, the size of the land, and the local regulations, ground mounts can cost 20-30% more than roof-mounted systems.
Additionally, for a ground mount installation, land availability and zoning regulations can impact the total cost. In some areas, permits may be needed for land use or environmental impact assessments, further adding to the complexity and expense of the project.
On the other hand, roof-mounted systems generally have lower upfront costs. Since the roof of an existing building is already in place, there is no need for additional land clearing, excavation, or structural foundation work. The mounting system, though still a crucial part of the installation, is typically simpler, as it involves attaching rails to the roof trusses to support the panels. This makes labor costs lower for roof installations, reducing the overall cost. Depending on the size of the system and the roof's condition, a roof-mounted solar system can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $25,000 for a typical residential installation, compared to $15,000 to $30,000 (or more) for a comparable ground mount system.
Long-Term Maintenance and Additional Costs
While ground-mounted systems have higher installation costs, they often have advantages when it comes to maintenance and long-term durability. Ground mounts are typically easier to access for cleaning and repairs, which can be important if you live in an area prone to dirt, dust, or debris. The panels can be adjusted to optimal angles without the constraints of roof shape, and the ground mount structure is usually less likely to experience wear and tear from weather-related issues like snow or heavy winds.
However, ground-mounted systems are not without their challenges. The mounting structures themselves can be vulnerable to environmental damage. For instance, in areas with heavy snowfall, the snow accumulation can cause damage to the frames or affect panel efficiency until it’s cleared. Similarly, ground-mounted systems are susceptible to potential wildlife interference, especially in rural or forested areas. Over time, the cost of maintaining these systems—such as replacing damaged frames or clearing debris—can add up.
Roof-mounted systems, conversely, require less maintenance because they are more sheltered from the elements and do not face the same wear and tear as ground mounts. However, accessing the roof for maintenance can be a challenge, particularly if the roof is steep or difficult to reach. This means that cleaning the panels or making repairs might require professional services, which can add additional costs over time. Moreover, roof-mounted panels can occasionally cause roof damage, particularly if improperly installed, leading to potential repairs or leaks. Homeowners need to ensure that their roof is in good condition before installation to avoid extra costs associated with roofing repairs.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
One of the most compelling reasons to choose a ground mount system is the ability to maximize energy efficiency. Ground-mounted solar panels are typically installed on adjustable frames, allowing for better optimization of tilt angles and panel orientation. This means they can capture more sunlight, which leads to higher energy yields. Additionally, ground mounts are less likely to experience shading from trees, nearby buildings, or other obstructions, which can be a major limitation for roof-mounted systems, particularly in densely populated urban areas.
Roof-mounted systems are limited by the orientation and slope of the roof. In some cases, a roof may not face directly south (in the northern hemisphere), reducing the panels' energy efficiency. Roof shading from nearby trees, chimneys, or other buildings can also significantly affect energy production. Furthermore, aesthetic concerns often influence how many panels can be installed on a roof, which can limit the total energy capacity of the system.
That said, modern roof-mounted systems can still perform well, especially if the roof faces the right direction (typically south-facing for maximum sunlight in the northern hemisphere) and if shading is minimal. Solar panel technology continues to improve, and more efficient panels can help compensate for some of these limitations. However, in terms of sheer energy potential, ground-mounted systems typically come out ahead.
Aesthetic and Space Considerations
For homeowners, aesthetic considerations can play a major role in the decision-making process. Ground-mounted solar systems, while efficient, are visible from a distance and can potentially alter the appearance of the landscape. In suburban or urban settings, this might be an issue if homeowners are concerned about the visual impact of the panels. In contrast, roof-mounted systems are less noticeable, especially if the panels are sleek and blend into the roofline.
Moreover, space availability is a key factor in the decision. For homeowners with limited yard space, a roof-mounted system may be the only feasible option. Conversely, if you have a large plot of land with plenty of open space, a ground-mounted system might be the better choice, as it offers greater flexibility in terms of panel positioning and energy optimization.
Choosing between a ground-mounted and a roof-mounted solar system ultimately depends on your specific circumstances—ranging from your budget and the amount of available space to the aesthetic impact and energy needs. While ground mounts are generally more expensive to install due to the added costs of land preparation, materials, and labor, they offer better long-term energy performance, easier maintenance, and more flexibility in system configuration. On the other hand, roof mounts tend to be more affordable initially, especially for residential properties, and come with less land disturbance, but they may face limitations in energy efficiency due to roof angle, shading, and space constraints.
Ultimately, it’s essential to weigh the upfront costs against the long-term benefits. For those with sufficient land and a desire for maximum efficiency, ground-mounted solar panels may be the optimal choice. For homeowners with limited space or a desire for a less intrusive installation, roof-mounted systems can offer a cost-effective and aesthetically pleasing solution. As solar technology continues to advance, both options will likely become even more efficient, allowing for more customization based on individual needs and environmental factors.
